Blockchain technology could turn out as one of the breakthrough inventions of the 21 century. Visionaries predict that blockchain could change the world just as the internet did, maybe even more. It could provide the technological infrastructure for the next wave of digital adoption and disrupt entire industries and business models like the World Wide Web did over the past 20 years.

Cryptocurrencies have already emerged as an entirely new asset class. As this new asset class moves more into the mainstream, businesses are now developing financial products for cryptocurrencies – one of them is crypto lending.
On crypto lending platforms, users will find two offerings:
-
Crypto-backed loans: Borrowers deposit cryptocurrencies as collateral and receive a loan in another cryptocurrency or fiat currency.
-
Crypto Savings accounts: Savers can deposit cryptocurrencies in savings accounts and receive interest in return.
Crypto lending explained: How crypto loans work
When borrowers apply for a loan with their bank, they first have to prove their creditworthiness by providing at least their source of income and credit history. On crypto lending platforms, borrowers only need to deposit cryptocurrencies (e.g. bitcoin) as collateral to get a loan (e.g. in fiat currency like euros or USD or stablecoins). That means borrowers make a conscious decision not to sell their cryptocurrencies but to pledge them as collateral so that they can retrieve them later – similar to a pawnshop. A better comparison is traditional securities-based-lending: An investor deposits a security, for example, a stock, as collateral with a broker or a bank and receives a loan in return.
You might be wondering why a borrower doesn't just sell his cryptocurrencies to get liquidity?
For "hodlers" (long-term crypto investors) who expect crypto prices to rise, crypto loans are a way to get cash without selling their cryptocurrencies. It's also a way to avoid paying capital gains taxes, which they might have to pay if they sold their cryptocurrencies.
But hodlers are just a minority among crypto lending borrowers. The main group of borrowers is institutional investors and businesses that work with cryptocurrencies, for example, crypto mining farms. These companies often have limited access to traditional debt capital markets, making the cost of capital in the crypto industry significantly higher compared to Wall Street. The reason is that the laws governing the new asset class are not yet well-developed in many jurisdictions, so it's difficult for banks to price the business models of crypto companies. In some cases, crypto companies can't even open a bank account because banks do not want to take regulatory risks by dealing with these customers. Crypto lending thus provides a way for crypto companies to obtain funding at a reasonable price.
To avoid misunderstandings: Crypto lending is not the same as P2P Lending. P2P Lending usually finances individual projects and often does not require collateral – and certainly not in the form of cryptocurrencies.
Another thing to keep in mind when talking about crypto lending is the difference between CeFi ("Centralized Finance") and DeFi ("Decentralized Finance") providers. Centralized providers are owned and run by private companies. Decentralized platforms, on the other hand, are based on a blockchain protocol developed by a community rather than a private company. In other words: If you give your cryptocurrencies to a CeFi platform, you trust a company; with a DeFi-platform, you trust in the protocol. It would help if you understood the differences between the two before choosing a platform, as both have their pros and cons.
How The Crypto Community Got Divided Into Two Halves: CeFi Vs. DeFi - Forbes #blockchain #ethereum https://t.co/k1rAjXOQen
— Blockchain Campaign (@BlkChnCampaign) November 20, 2020
Forbes article on Cefi vs. Defi
How does crypto-collateralization work?
When taking out a crypto-backed loan, you have to agree to a certain Loan-to-Value ratio. The Loan-to-Value ratio (LTV) determines the amount of collateral required. This ratio can differ depending on the platform. It describes the ratio of the loan amount to the collateral: With an LTV of 50%, the loan amount will be half of the deposited collateral, which means the borrower must deposit cryptocurrencies worth twice as much as the loan amount.
If the LTV then rises above 50% during the loan term – for example, because the market value of the pledged collateral drops – the platform will trigger a margin call. It will then request the borrower to post additional collateral within a period of time (e.g. 72 hours) to restore the LTV agreed in the loan contract. Alternatively, the borrower can also repay his loan balance until the pre-agreed LTV is restored.
If the borrower does not comply with this request - or if the LTV exceeds a critical value (on most platforms, this value is between 80% and 90%) - the lending platform will automatically liquidate a portion of the collateral and use it to repay the loan until its value compared to the value of the collateral is reduced to the pre-agreed safety margin. This automated mechanism protects the platform provider and its users from default risks because the collateral always exceeds the loan amount and is automatically liquidated as soon as the value of the collateral comes close to the loan balance. Thus, crypto-backed loans are always overcollateralized.
What are Crypto Savings Accounts?
Crypto lending platforms finance their loans through the collateral posted by borrowers and the cryptocurrencies deposited by savers in crypto savings accounts. These crypto savings accounts usually carry a much higher interest than traditional bank accounts. Savers usually receive daily, weekly or monthly interest, depending on the platform. They can usually deposit free-floating cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, stablecoins (cryptocurrencies that are pegged to a stable asset such as the U.S. dollar or gold), or in some cases also fiat currencies such as the U.S. dollar or the Euro. The conditions and terms of crypto savings accounts can differ significantly from platform to platform.
Crypto savings accounts thus offer you the opportunity to generate passive income. While you can hardly get any interest on bank deposits anymore – at some banks, the rates are even negative – double-digit returns are possible on crypto savings accounts. Most lending platforms offer interest rates ranging from 4% to 12% – compare that to 0.5% on bank deposits or to government bonds that no longer pay any interest at all. The opportunity to earn high rates in a zero-interest rate environment is attractive for both savers and institutional investors. However, this higher return also comes at a higher risk, such as the price fluctuations of the collateral, the insolvency risk of the platform provider, and technical risks.
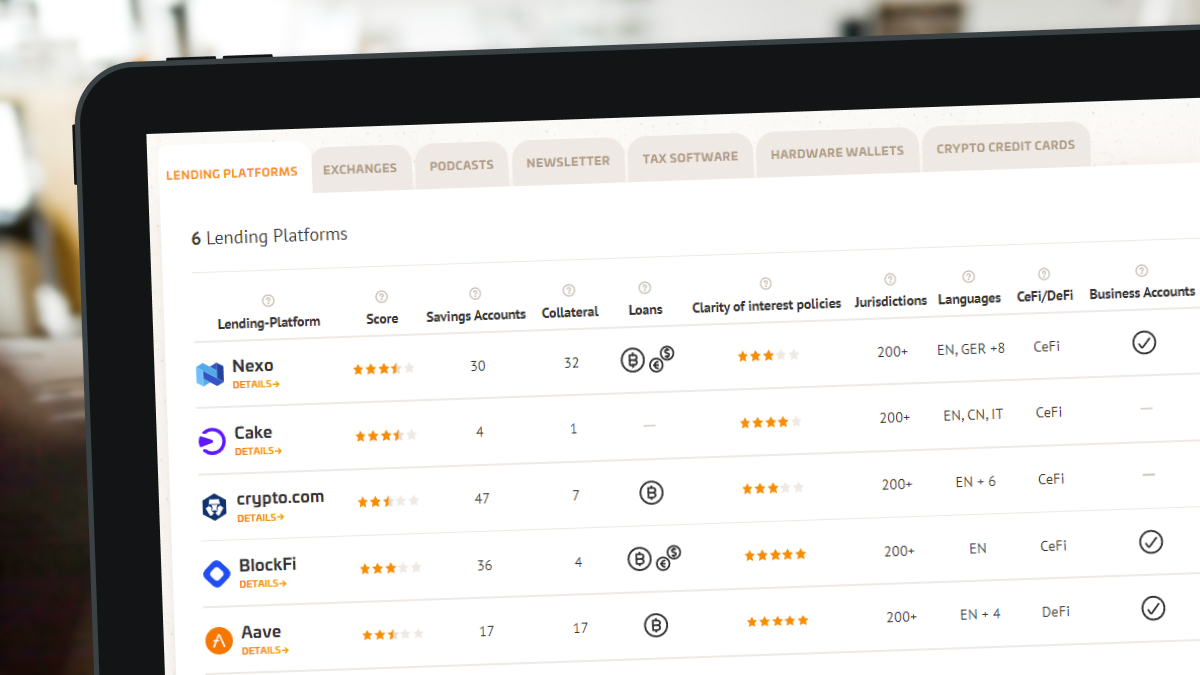 CryptoStudio compares the leading platforms in detail
CryptoStudio compares the leading platforms in detail
High-interest rates in crypto lending: a simple explanation
We already touched on the cost of capital in the crypto ecosystem above, which partly explains the high interest rates. Take, for example, crypto mining farms: Those are companies that make money by mining new bitcoins. If miners expect crypto prices to increase, they may not want to sell their cryptocurrencies at the current price – so they want to earn interest on their cryptocurrencies while holding them – but they also need liquidity in the form of fiat currency to run their mining farms. Since they cannot get a loan (or only a very expensive one) from traditional banks, crypto loans are an attractive funding source despite higher interest rates. The comparatively higher rates on these loans are less of an issue for the miner, as they can also invest a portion of their cryptocurrencies at higher interest rates in crypto savings accounts. The math works!
As the rates on loans are high, platforms can also pay high rates on savings accounts. But there is some more to it. Before we delve into that, you need to understand how exactly crypto lending platforms earn money:
Crypto lending platforms receive cryptocurrencies from both savers and borrowers. Let's go back to the comparison with a securities broker: Here, an investor buys a security and deposits it with a broker, and the broker then lends this security to traders and institutional investors who in turn pledge collateral and pay a fee. As the broker makes money this way, he can offer lower trading fees than banks. In traditional financial markets, this form of collateralized securities lending is considered a relatively safe transaction, and most major brokers and financial institutions are involved.
Crypto lending platforms operate in a similar way: They lend cryptocurrencies to investors in the form of overcollateralized crypto loans through their platforms, as already explained above. They also lend cryptocurrencies to institutional investors in over-the-counter transactions, just like securities brokers. These institutional investors include firms like crypto exchanges, market makers, or hedge funds that need cryptocurrencies for their day-to-day business, for example, to provide liquidity for traders or short-selling.
So the key reason why you can earn such high interest rates on your crypto savings is that the platforms can earn money by lending your cryptocurrencies to institutions. For the institutions themselves, it can be well worth paying high fees for borrowing cryptocurrencies. As crypto markets today are not yet as efficient as traditional financial markets, there are significant profit margins. Take arbitrage trading, for example. Liquidity differs from exchange to exchange, meaning the same cryptocurrency will sometimes trade at different prices. Traders can then buy it at a low price on one exchange and sell it more expensively on another. Such structural inefficiencies can lead to arbitrage gains of 10% - 20%. If traders then buy the necessary liquidity from crypto lending providers for 8% interest, they are still getting a good deal.
It is also important to remember that people in the West are generally used to low interest rates. Even if the interest rates for crypto lending seem very high from a European or U.S. point of view, they are actually moderate in international comparison. In many emerging and developing markets, double-digit interest rates - for both savers and borrowers - are standard.
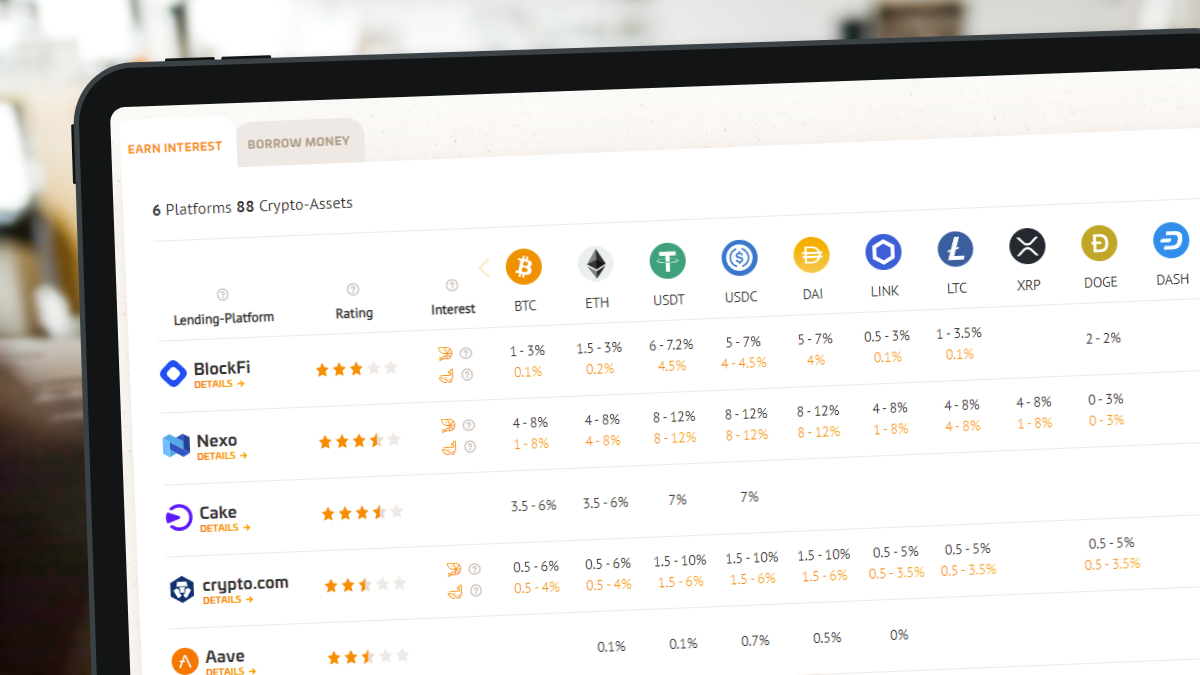 Crypto lending interest rates in our review table
Crypto lending interest rates in our review table
Crypto lending is the next evolutionary step of the lending market
Crypto lending plays an increasingly important role in the crypto ecosystem as it provides liquidity for market participants. And besides that, crypto lending also connects the crypto and the traditional financial industries, which means it also has economic relevance beyond the crypto industry. Investors of all types can use crypto lending to generate passive income and participate in the new asset class – without the high volatility of Bitcoin investing.
The technological features of the crypto asset class, and its high degree of automation, offer critical advantages over traditional banking. Since no credit check is required, the entire process is much faster and incurs hardly any costs. Additionally, crypto lending also increases financial inclusion: Those who have a poor credit history, those who cannot (or do not want to) provide their sources of income, or those who do not have access to the banking system - for example, borrowers from emerging and developing countries - can still take out crypto-backed loans without any requirements other than pledging crypto collateral.
Crypto lending will become much more relevant for the overall economy once assets are tokenized on a large scale – and it is only a matter of time until that happens. Already today, it is possible to digitally represent real estate, bonds, stocks, and nearly any other asset as security tokens (blockchain-based securities). Once more assets are tokenized, investors can deposit these assets as loan collateral. Instead of mortgaging your house, you could then pledge a real estate token that digitally represents your house. If everything is digital, no more bureaucracy will be required. You don't need to pay for a valuation of your house or for a lawyer to draft a contract; everything happens digitally and within fractions of a second. All of that may sound like science fiction, but it's not; it's already technically feasible today.
Jay Clayton, Chairman of the US Stock Exchange Commission.















.png)